
The mechanics of inverter generators are slightly more complicated than conventional portable generators. There are more parts involved in delivering the final electrical output.
Many inverter generators also run on fossil fuels. In addition to the drawing power from the fuel tank, inverter generators also have a battery, alternator and inverter.
The power from the engine is a high frequency AC current which is then converted into DC current by the alternator. That DC current is then converter back into AC current by the inverter.
Like with conventional portable generators, inverter generators also have an output of 120 volts at 60 Hertz. However, because of the extra steps in the electricity production, the current of an inverter generator is much more stable.
In other words, there is less harmonic distortion which is why inverter generators are said to produce ‘clean electricity’. The quality of electricity produced by inverter generators is comparable to the quality of electricity that you receive from the mains electrical supplier.
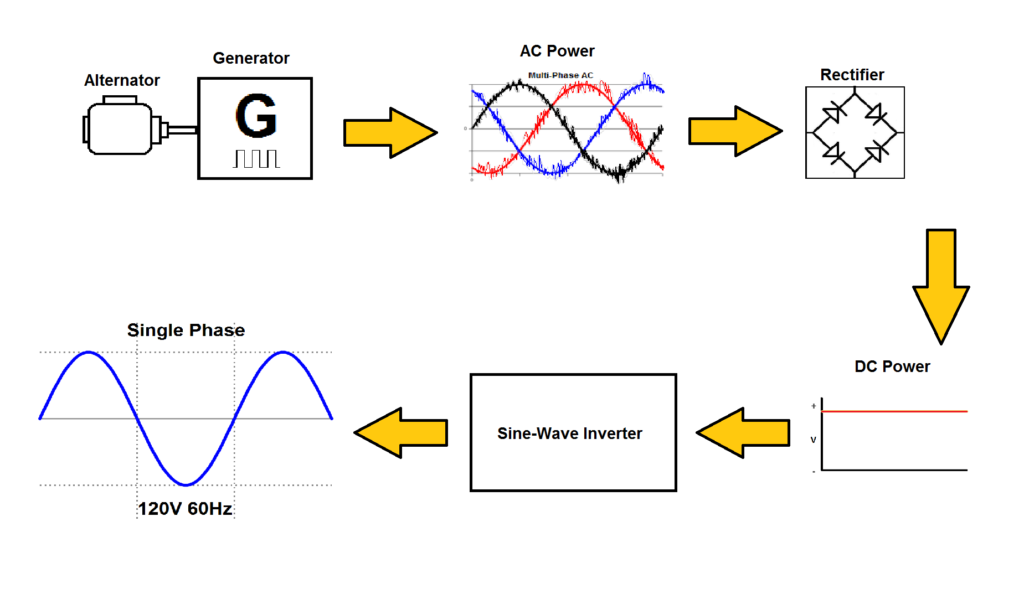
The clean electricity is possible because of two factors. The first factor is that the initial AC current in an inverter generator is at a high frequency which gives more electrical energy.
The second factor is the inversion of the DC current back into AC current. The mechanics of an inverter generator has more control over the AC frequency which lets it provide a very stable sine wave.
The greater control over the electrical output makes inverter generators quite energy-efficient. It can adjust its voltage to what is exactly needed by the connected load while still maintaining an rpm of 3600.
The stable current is also one of the main reasons why inverter generators are quite silent compared to conventional portable generators.
